Sudden cardiac arrest, learn CPR first aid
Article tag: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation medical first aid model
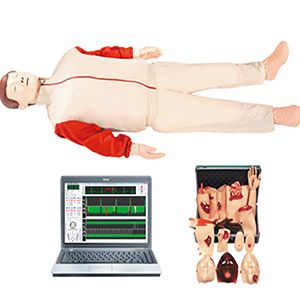
In modern times, more and more people will have physical diseases. Cardiopulmonary disease is one of the most serious diseases that threaten people's life and health. So, how to do CPR in cardiac arrest? The following cardiopulmonary resuscitation simulator manufacturers will share with you, hoping to help you.
...
In modern times, more and more people will have physical diseases. Cardiopulmonary disease is one of the most serious diseases that threaten people's life and health. So, how to do CPR in cardiac arrest? The following cardiopulmonary resuscitation simulator manufacturers will share with you, hoping to help you.
For patients with cardiac arrest, if they do not receive treatment for more than 5 minutes, it will lead to irreversible death of brain cells, and it is difficult to rescue them after more than 10 minutes. If cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed within 5 minutes, the patient may still be rescued, also known as "5 minutes of life and death". So, how to do CPR?
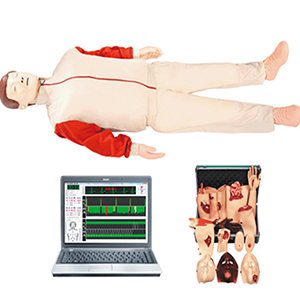
1. First, determine the patient's consciousness. Call him out loud, or shake him to see if there is a response. Move closer to his nose, mouth, and feel for breath. Touch his carotid arteries to see if there is a pulsation. Do not touch both carotid arteries at the same time, as it is prone to danger.
Open the airway. Place the patient in a supine position. Comatose people often have airway blockage due to the tongue falling back. At this time, the rescuer should kneel on the side of the patient's body and press down on the forehead with one hand. The other hand holds the chin and lifts it up. The standard is that the line connecting the chin and the earlobe is perpendicular to the horizon, which means that the airway has been opened.
2. Artificial respiration. If the patient is not breathing, immediately give mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration twice, then feel the carotid artery, if you can feel the pulsation, then give artificial respiration only.
Method: It is best to find a clean gauze or towel, which should be in the patient's mouth to prevent bacterial infection. The rescuer pinches the patient's nose with one hand, inhales heavily, holds it, leans over quickly, wraps the patient's mouth with his mouth, and quickly blows in the gas. At the same time, the rescuer's eyes need to observe whether the patient's thorax is expanded due to the infusion of gas. After blowing the gas, release the hand holding the nose and let the gas exhale, thus completing a breathing process. An average of 12 rescue breaths were performed per minute.
3. External chest compressions. If the patient has no pulse to begin with, or if the patient is still not palpable after one minute of rescue breaths, perform chest compressions.
Method: The rescuer must first find the place to be pressed. From the bottom to the middle of the body, feel the junction of the ribs on both sides of the lowermost edge, called the xiphoid process. With the xiphoid process as the point, define the position of two transverse fingers on the sternum, which is the middle and lower third of the sternum. At the junction, here is the implementation point. The rescuer stacks one hand on the back of the other hand, interlaces his fingers, places the base of the palm in the position just found, and presses down vertically with the strength of the upper body, the sternum sinks about 4-5 cm, and the arms must be straight , can not bend, quickly lift up after pressing down, the frequency is controlled at 80-100 times per minute.
The force must be controlled, not too much force, because too much force can easily cause rib fractures, which will cause the ribs to puncture important organs such as the heart, lungs, liver and spleen. The bones of the elderly are inherently fragile, and more attention should be paid to them.
The ratio of single rescue and double rescue. For single rescue, for every 15 artificial breaths, do two chest compressions; for double rescue, do two chest compressions for every 10 artificial breaths.
Indication to discontinue CPR. Monitor the patient's vital signs at all times. Touch the patient's hands and feet. If the temperature rises, further touch the carotid artery and stop cardiopulmonary resuscitation if there is a pulse, and send the patient to the hospital for further treatment as soon as possible.
If you have more questions about CPR, you can call the CPR simulator manufacturer. We will serve you wholeheartedly and look forward to your call.

Marketing Center
Hong Kong, ChinaProduction Base
Shanghai, ChinaProducts
Contact Us
 Address: Hong Kong, China
Address: Hong Kong, China
 Phone:+86 19937901373
Phone:+86 19937901373
 Email:sophia@adahealthy.com
Email:sophia@adahealthy.com
 Mobile:+86-0379-65160607
Mobile:+86-0379-65160607
举报邮箱:sophia@adahealthy.com
举报电话:+86 19937901373








