Nursing methods and precautions after successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation

Timely and correct follow-up care for successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation is an important part of the recovery of health for patients with cardiac arrest. This is because, although the patient seems to have recovered his blood spontaneous circulation and his related ...

Timely and correct follow-up care for successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation is an important part of the recovery of health for patients with cardiac arrest. This is because, although the patient seems to have recovered his blood spontaneous circulation and his related physical signs have stabilized after successful CPR on the surface, in fact, the patient is not really safe, and his accidental mortality rate is still very high. High, because 72 hours after initial successful CPR is still difficult to judge. How to reduce the multiple organ failure caused by unstable hemodynamics, which eventually leads to death, as well as the delayed death caused by brain injury, is very important.
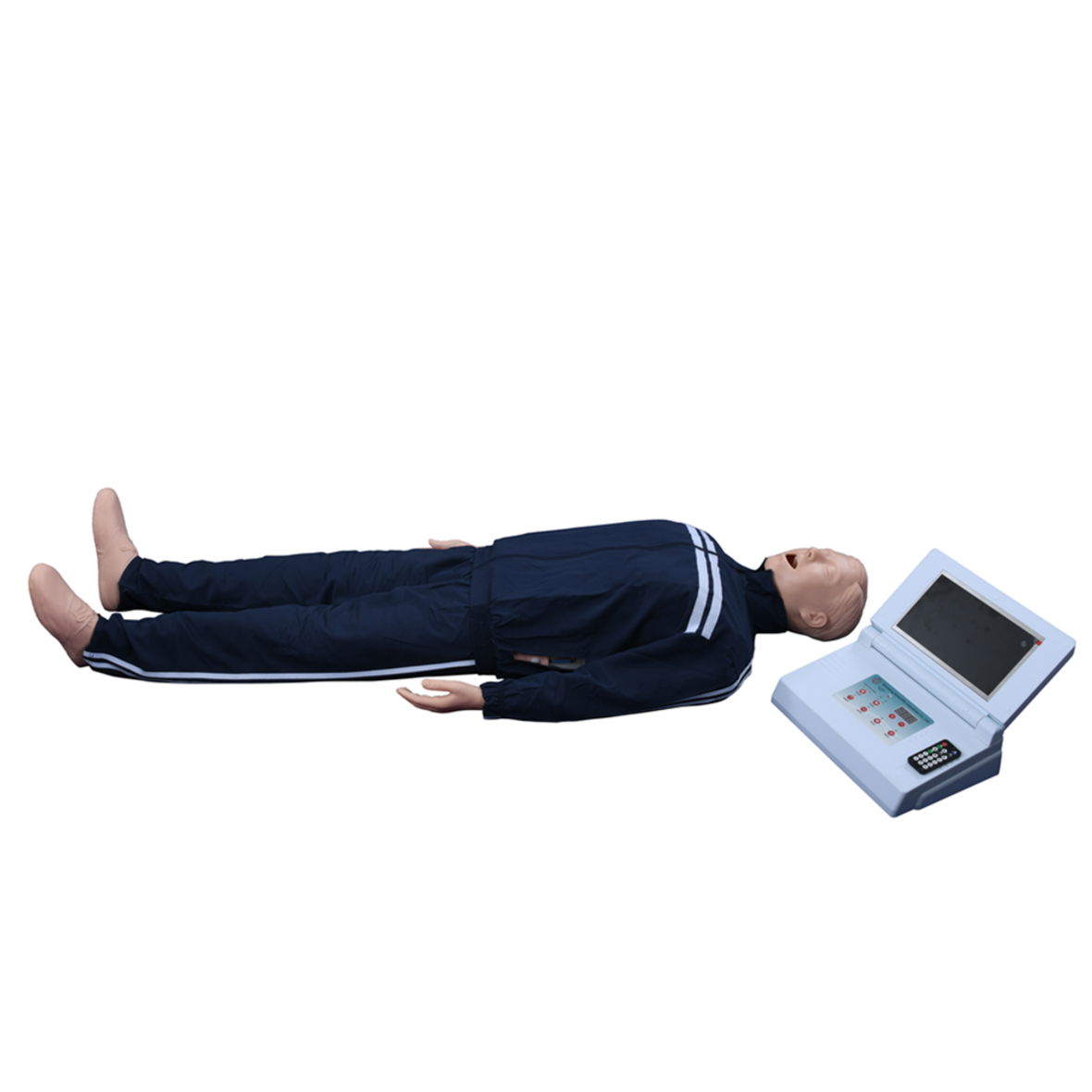

Moreover, for people in the social sense, the recovery of nervous system function after CPR is particularly critical. The research results of neurology, hemodynamics, respiration and metabolism in patients with successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation after cardiac arrest are described accordingly to explore effective measures to improve post-CPR nursing care.
Due to brain trauma and cerebrovascular accidental ischemic-hypoxic encephalopathy caused by cardiac arrest itself, although patients can recover spontaneous circulation after CPR, they may still experience coma or reduce their responsiveness to external stimuli. After the initial transient cerebral hyperperfusion after the recovery of autonomic blood circulation, cerebral blood flow will decrease or even no-reflow phenomenon due to blood microcirculation dysfunction, which may also occur in the case of normal cerebral perfusion pressure.
For such patients, proper cerebral perfusion pressure and effective cerebral perfusion must be ensured by maintaining normal or slightly elevated mean arterial pressure and reducing intracranial pressure. Epilepsy often occurs in patients after prolonged cardiopulmonary resuscitation due to ischemia and hypoxia in the human cerebral cortex. However, epileptic seizures will increase the oxygen demand of the brain and the oxygen consumption of the body, thereby damaging brain cells and aggravating brain edema. Therefore, definite epileptic seizures must be controlled in time. Drugs can be selected from intravenous diazepam, hibernating mixture, debakin, etc. And it is necessary to add subsequent anticonvulsants to maintain remission and then slowly reduce the dose. At the same time, if conditions permit, EEG monitoring at the bedside can be continued to detect and treat epileptic seizures without obvious clinical symptoms as soon as possible.

Marketing Center
Hong Kong, ChinaProduction Base
Shanghai, ChinaProducts
Contact Us
 Address: Hong Kong, China
Address: Hong Kong, China
 Phone:+86 19937901373
Phone:+86 19937901373
 Email:sophia@adahealthy.com
Email:sophia@adahealthy.com
 Mobile:+86-0379-65160607
Mobile:+86-0379-65160607








